Progress towards Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD)
Coillte is aware of its direct and indirect impact on the climate in terms of how the Coillte estate is managed and the products it produces. Coillte also acknowledges the responsibility to decarbonise its own operations, influence positive climate solutions across the forest industry and Coillte’s supply chain, and to support Ireland’s transition to a low carbon economy.
In recognition of the growing climate crisis, Coillte declared its support for the Financial Stability Board (FSB) Task Force on Climate[1]related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) in 2021. Coillte’s alignment with the TCFD framework supports the organisation in gaining a better understanding of its climate-related financial risks and opportunities. Trees grow on average between 40 to 100 years, and as such Coillte is committed to ensuring that careful consideration is given to the possible future climate change scenarios. Therefore, a long-term strategy, strong governance, pro-active risk management and measurement of Coillte’s progress are crucial for the sustainability of the organisation.
Over the last three years, Coillte has made significant progress across all TCFD disclosures. In 2023 Coillte’s Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions were published, and an evaluation of its Scope 3 emissions profile commenced. In December, the Coillte Board approved emission reduction targets for Scope 1 and Scope 2 which are published for the first time in this report. In 2023, a climate scenario analysis was also finalised with various possibilities tested against Coillte’s strategy resilience.
Through the disclosures in its Annual Report, all TCFD recommendations have been addressed. However, Coillte recognises there are still opportunities across each of the four TCFD pillars to improve and provide more detail directly aligned to the disclosure requirements, e.g. calculating and disclosing Scope 3 emissions.
Coillte is committed to continuous improvement across all 11 TCFD recommendations, and to achieving full compliance with the framework by the end of 2024.

NewERA Climate Action Framework
The Climate Action Framework for the Commercial Semi-State Sector was approved by the Government in July 2022. The Framework consists of five commitments that each Commercial Semi-State Body should adopt:
- Governance of Climate Action Objectives.
- Emissions Measurement & Reduction Targets.
- Measuring and Valuing Emissions in Investment Appraisals.
- Circular Economy and Green Procurement.
- Disclosures in Financial Reporting.
Since the adoption of the framework by the Coillte Board in Q4 of 2022, Coillte has made significant progress against most of its commitments.
Governance
The Group Sustainability Governance Structure is fully established with the Group Sustainability Committee being the key link between divisional Green Teams, senior management and the Board.
Circular Economy
A policy and strategy is being developed and will be finalised in 2024. The key principles are outlined in Coillte’s Annual Report.
Investment Appraisal
In 2023, Coillte completed greenhouse gas (GHG) investment appraisal training organised by SEAI and plans to include carbon appraisals in all future investments.
GHG Emissions
A baseline assessment of Coillte’s GHG emissions across Scope 1 and Scope 2 was completed in 2023. Key carbon reduction pathways were identified, and targets were approved by the Coillte Board in December 2023. Coillte is currently finalising Scope 3 assessment.
Climate Scenario Analysis (SCA)
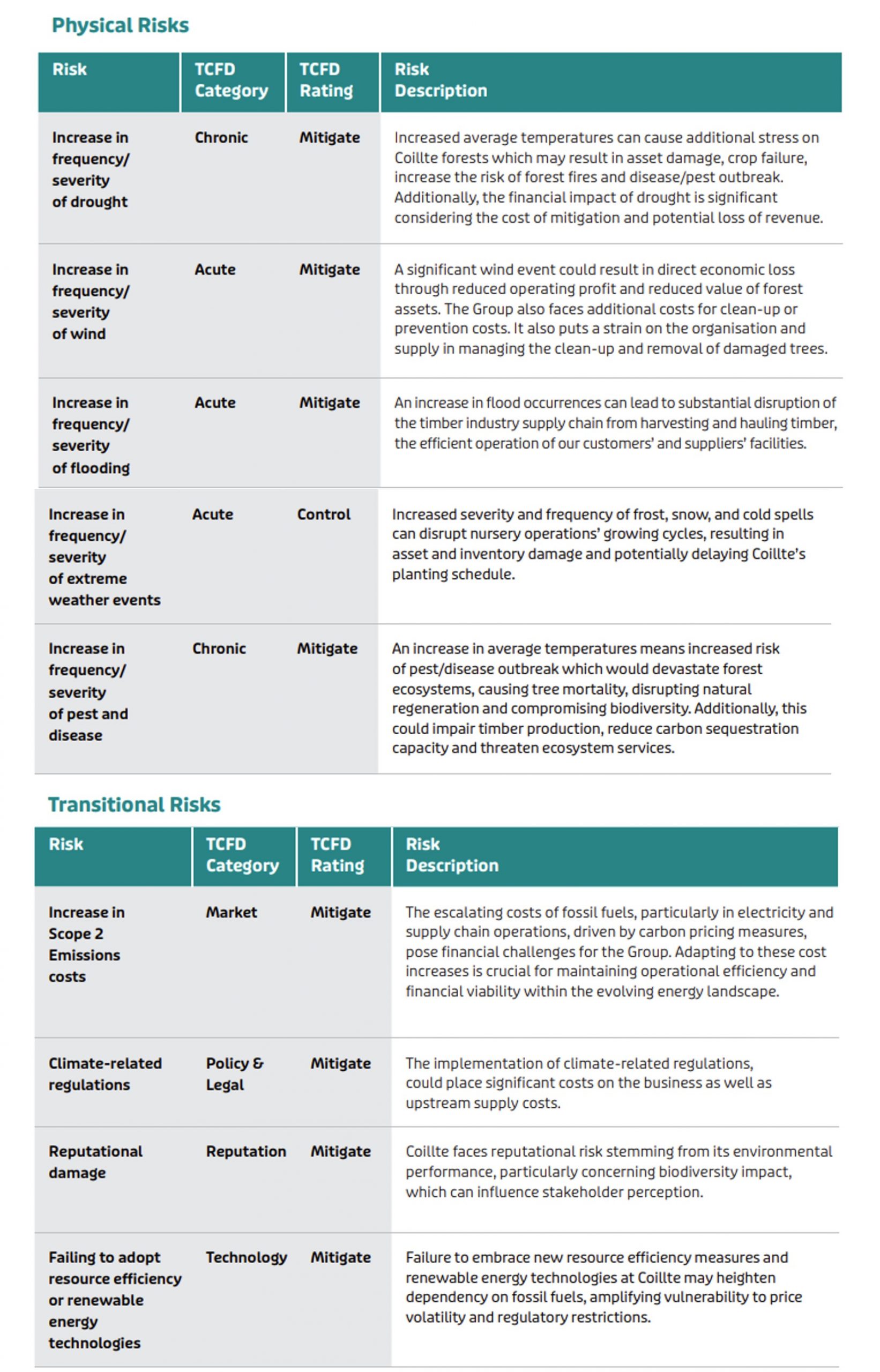
In line with TCFD requirements, a CSA project was conducted in 2023. As part of the CSA Coillte considered climate related physical risks and transitional risks as well as opportunities. Coillte provides reports to NewERA on its progress against Climate Action Framework recommendations twice yearly using the online Framework Reporting Template.
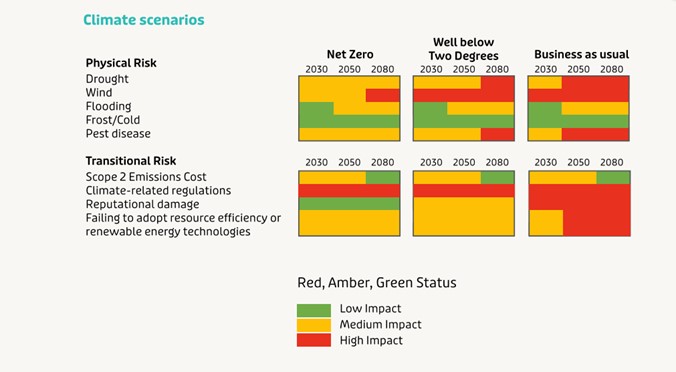
As part of its continued commitment to understanding climate-related risks and opportunities, Coillte has conducted a comprehensive climate scenario analysis assessment. This analysis aims to deepen insights into potential climate impacts on Coillte’s business and operations and assesses the Group’s strategy resilience under various climate risks and opportunities, aligning with TCFD disclosures.
The climate scenario analysis involved forecasting financial impacts by utilising specific climate scenario variables. While models assume no proactive measures to minimise impacts, supply chain information and biological assets across the country have been used. The identified hazards included flooding, changing temperatures and wind.
For the 2023 analysis, collaboration across the organisation was key, utilising the wealth of knowledge and experience within the Group. Physical risks, transition risks, and transition opportunities resulting from climate change were considered. The scenario selection adhered to the TCFD recommendations, industry best practices, and the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) climate scenarios.
The selected IPCC Representative Concentration Pathways (RCPs) used were:
- RCP2.6 (~1.5°C) – Net Zero
- RCP4.5 (~2.0°C) – Well below Two Degrees
- RCP8.5 (~3.5-4.5°C) – Business as usual
These pathways represent varying greenhouse gas emissions and global warming levels until 2100, as outlined in the IPCC Assessment Reports (AR5 and AR6)
Risk Assessment Process
Data collection involved leveraging Coillte’s existing risk framework, past annual reports, and relevant documents along with a peer and sector review. Every risk and opportunity identified was evaluated, with discussions and assessments involving management from across the business.
The financial impact of selected risks and opportunities was assessed across short, medium, and long-term horizons and the IPCC scenarios.
The scenario assessment identified significant climate-related opportunities across the Group. These include access to lower interest rates from ESG and Green funding, increased demand for afforestation, climate projects such as peatland redesign, demand for renewable energy, and growing demand for low carbon wood products, particularly in the housing and construction sectors.
Simultaneouly, Coillte recognises the opportunity to enhance biodiversity, adopt new technologies to lower our carbon footprint and enhance our reputation.
Energy Management
Coillte successfully completed its ISO 50001 Energy Management System surveillance audit in November 2023. There were no adverse audit findings and one opportunity for improvement.
Coillte uses a specialist software package to track and graphically present monthly energy bills by cost, kWh and carbon emissions for offices, nurseries and the company car and van fleet. This system also facilitates the compilation of monthly energy performance indicator reports. The company car and van fleet fuel efficiency are analysed per vehicle.
Realtime energy consumption is being tracked for a broad range of equipment in Ballintemple Nursery as well as Coillte’s Head Office in Newtownmountkennedy Co. Wicklow. Sub-metering is also being installed in Beyond the Trees Avondale, at Avondale Forest Park, Co. Wicklow. The energy consumption data for these three sites is presented on a cloud-based portal site.
MEDITE SMARTPLY has an overarching annual energy management plan that is structured by ISO 50001 and targets energy efficiency and energy reduction projects across its processes.
In 2023, the first full year of monitoring of SMARTPLY’s drying, energy and screening investment was completed and has led to notable enhancements in energy efficiency such as heat recovery, thermal efficiency, and electrical usage. One of the key criteria of the vendor selection process was to minimise energy, resulting in the procurement of optimal technologies and plant configurations. An additional objective of the project was to move from diesel to biomass as a fuel source. As a result, Scope 1 stationary CO2 emissions have been reduced.
Carbon Emissions
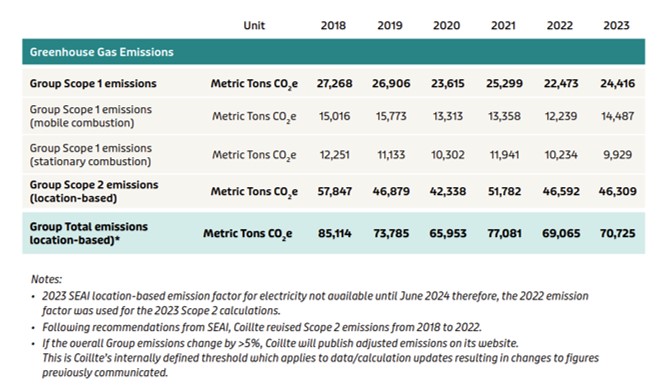
Coillte remains focused on its commitment to measuring and mitigating carbon emissions associated with its business and operations. In 2023, Coillte concentrated on Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions, using 2018 as the baseline year for calculations. Coillte adheres to the Greenhouse Gas Protocol (GHG Protocol) guidance, ensuring a standardised and credible approach to emissions measurement. The baseline emissions were established in 2018, and this methodology has been consistently applied to the years 2019 to 2023. The results of Coillte’s Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions are presented in the accompanying table.
Coillte’s total Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions were 17% lower in 2023 than in 2018. This change was driven mostly by the following three factors:
- Fluctuations in Scope 2 location-based emission factors influenced by the percentage of renewable energy available from the Irish electrical grid.
- Lower 2023 production volume vs. 2018.
- The implementation of energy efficiency initiatives, with the most significant impact being the construction of a new world-class drying, energy and screening system in SMARTPLY in late 2022 of which the full emission reduction benefit was observed in 2023.
In 2023, Coillte continued to engage in a pilot test of the GHG Protocol Land Sector and Removals Guidance. The GHG Protocol Pilot gave Coillte the opportunity to test the draft guidance and to provide suggestions for improvement for the final version.
In 2024, Coillte is planning to continue evaluating its Scope 3 emissions profile. Preliminary analysis using the GHG Protocol indicates that Scope 3 emissions may represent 75-80% of business overall emissions. Coillte is actively working towards a full quantification of Scope 3 emissions as part of its commitment to the Science Based Targets initiative.
Carbon Reduction Targets
In December 2023, the Coillte Board approved the Group’s near-term carbon reduction targets. Coillte is committed to reducing its Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions by 51% by 2030. The following key potential areas of focus were identified in order for Coillte to reduce its carbon emissions:
- Corporate Purchase Power Agreement to assist in the decarbonisation of electricity (Scope 2).
- Sustainable Transport and Mobility Strategy to address diesel related activities in Scope 1 and Scope 3.
- Close co-operation with Coillte’s supply chain, to understand related climate commitments.
- Continuous optimisation of Coillte operations and increased energy efficiency.
- Green procurement as the main vehicle to decarbonise supply chain emissions.
While Coillte is still in the process of assessing its carbon footprint, steps have already been taken to address the main emissions sources. The organisation is continuously working on various energy improvement initiatives and is fully certified to ISO 50001 standard.
In 2023, the Sustainability Team expanded with the appointment of a Sustainability Data Analyst, who will assist in the creation of a robust data management strategy to complement compliance and governance requirements. The Group is also carrying out research projects which will help to increase the circularity of processes and reduce carbon emissions associated with its supply chain.
Sustainable Transport
Coillte’s Sustainable Transport & Mobility Programme was initiated in 2023. The Coillte business greenhouse gas emissions assessment found that over one quarter of all Coillte’s business emissions are associated with mobile combustion and fuel related activities. Therefore, decarbonisation of Coillte’s forest operations, haulage, distribution and mobile equipment, has become a key objective for making the business more sustainable.
The Sustainable Transport & Mobility Programme aligns with the Irish Climate Action Plan, the Climate Action Framework for commercial semi-state companies, and the Department of Transport’s Road Haulage Strategy 2022-2031, emphasising an Avoid-Shift-Improve approach to transport decarbonisation.
Coillte’s ambition is to achieve decarbonisation in Scope 1 (mobile combustion) and Scope 3 (fuel-related activities, upstream and downstream distribution) by trialing and incorporating various technologies, and through green procurement and sustainable supply chain transformation. This involves creating a Sustainable Logistics Roadmap in 2024 which will support the pathway to achieving carbon reduction targets by 2030. The key enabler for the delivery of Coillte’s ambition and carbon reduction targets will be the Sustainable Transport and Mobility Strategy with specific actions identified to 2030.
This strategy identifies four key pillars:
Green Public Procurement
Incorporating green criteria into public procurement provides an opportunity to convert environmental policy objectives on carbon reduction, air and water quality, and waste reduction into delivered actions.
Data Management Systems
Coillte intends to leverage advanced data analytics to provide an understanding of the sustainability challenges that need the most urgent attention to underpin decisions on how to address specific issues.
Pilot-Learn-Deliver approach
Sustainable supply chain transformation can be achieved through systemic thinking and a whole team effort to embrace complex challenges and acquire the knowledge to procure and implement sensible solutions. Therefore, it is important to carry out feasibility studies and develop the business case that identifies the viability of sustainability solutions. In 2023, we commenced this process with the Hydrogenated Vegetable Oil (HVO) Trial.
Stakeholder Collaboration & Engagement
Effective collaboration that facilitates the exchange of unique perspectives and ideas can potentially result in more innovative solutions to the sustainability challenge. These strategic pillars provide a foundation for objectives and actions which will help to create a detailed Sustainable Logistics Roadmap for Coillte to 2030.
Bio and Circular Economy.
The bioeconomy refers to economic activity derived from the use of biological resources such as wood to produce products, while the circular economy refers to economic activity based on the use, reuse and recycling of resources and materials.
The forestry and forest products sectors are among the primary examples of functioning bio and circular economic activities. As trees grow, they sequester or sink carbon, which is stored in their wood. When trees are harvested and converted into long life wood products for construction and other uses, they store that carbon in buildings and products.
Wood products can substitute and replace non-renewable high carbon products. This sink, store and substitution of carbon has a triple effect on climate, while the loop is completed by replanting to start the circular process all over again once the trees are harvested.
Wood products in construction have a major impact on decarbonising the built environment, by displacing high carbon construction materials with timber alternatives to support a circular economy.
Coillte’s aim is to use wood in a sustainable manner under the cascading principle of biological resource use, where the waste from one wood process is used to produce other products as follows:
- Wood is initially processed into high value long life, circular, carbon products such as construction products (sawnwood and engineered wood).
- Waste streams from primary processing (residual wood) is then used to manufacture wood-based panel products such as OSB, MDF, Wood Fibre Insulation and other products.
- Waste streams from the above are bio-refined to make high end products such as, fuel and chemicals.
- After use and re-use of these valuable natural resources, their potential end of life use will be to create heat or power.
This cascading model is in line with the ambition of the EU Green Deal, which aims to make Europe Net Zero by 2050.
Coillte works continually with its customers and partners including other Irish and EU companies, research institutes and academia to develop sustainable, circular and innovative wood products and to explore innovative technologies and solutions to develop lean processes for the future.
These include:
- Timber building systems - working with partners to explore how more Irish timber can be used in timber frame construction in general as well as to develop engineered wood products such as Cross Laminated Timber (CLT) to allow multistorey timber construction in Ireland.
- Bio-refining - an emerging technology to utilise the waste stream of wood to develop bio-chemicals, biochar, bioplastics and biofuels, and
- Bio-chemicals - the development of bio-chemicals and products to allow wood products to be more circular and to be re-used at their end of life.
Coillte’s forests and lands also support a vibrant bioeconomy through the production of bio services in the form of recreation, outdoor activities, water, clean air, carbon removal, biodiversity and other ecosystem services.